FALL 2016
FINAL EXAM
MONDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2016, 1530-1730
Name: __________________________________ Red ID ____________________ Grade: ________
Instructions: Open book, open notes. Use engineering paper. When you are finished, staple your work in sequence (1 to 5), and return this sheet with your work.
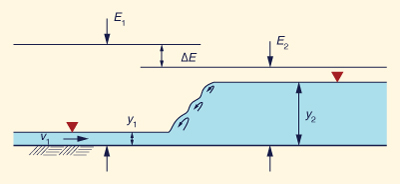
(20%) Calculate the initial and sequent depths y1 and y2 of a hydraulic jump, given unit-width discharge q = 0.12 m2/s, and energy loss ΔE = 0.6 m. Procedure: Assume a suitably low F1; calculate y2/y1, y1, v1, and a new F1. Compare new value with assumed value; if different, increment F1 a suitable amount and iterate, until a match is obtained. Show results in tabular form. Confirm with onlinechannel16.php
(20%) You are observing the rising flood stage of a major river in a study reach AB of length
L = 10 km. At your observation point at the downstream point B, the discharge is QB = 300 m3/s and the stage is rising at the rate of rB =3.2 mm/hr. The average surface width of the river in the study reach is W = 180 m. Estimate the present discharge at point A. How could this estimate be improved?(20%) A hydraulically wide channel is operating at Froude number F = 0.18. The unit-width discharge is q = 2.25 m2/s. What are two Langrange absolute celerities?
(20%) Teton Dam failed on June 5, 1975, in Idaho, releasing 2,000,000 cfs. At a distance of
100 miles downstream, the flow was estimated to be 50,000 cfs. What type of wave was most likely acting? Kinematic, diffusion, or dynamic? Why?
(20%) An irrigation canal has a mean velocity u = 0.7 m/s, mean flow depth d = 1 m, and slope
S = 0.005 m/m. Estimate the minimum time of gate opening To to minimize the possibility of a surge.