FALL 2017
SECOND MIDTERM
NOVEMBER 13, 2017, 1600-1650
Name: ______________________________ Red ID No. _______________________ Grade: ________
Instructions: Closed book, closed notes. Use engineering paper.
When you are finished, staple your work in sequence (1 to 4),
and return this sheet with your work.
(30%) A weir is located at the downstream end of a wide rectangular channel of bottom slope So = 0.0035 and dimensionless Chezy friction factor f = 0.0035. The unit-width discharge in the wide rectangular channel is q = 0.4 m3/s/m. Immediately upstream of the weir, the flow is subcritical, with depth 1.5 m.
- Calculate the Froude number of the normal flow in the upstream channel.
- Calculate the normal flow depth in the upstream channel.
- Calculate the normal flow velocity in the upstream channel.
- Calculate the length of the C1 water-surface profile.

- Calculate the Froude number of the normal flow in the upstream channel.
(30%) A hydraulically wide supercritical flow channel with So = 0.025 flows into a critical flow channel of So = 0.004. The dimensionless Chezy friction factor f is the same is both channels. The unit-width discharge is 2.2 m2/s. Find the length of the C3 water surface profile in the critical flow channel.
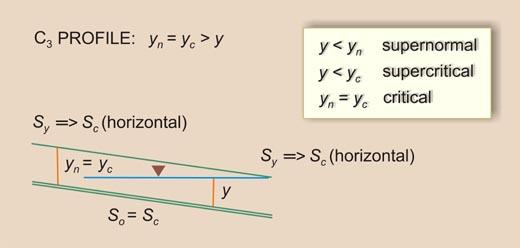
(20%) Please answer the following questions in a brief statement.
- When the water is clear of sediment, does it tend to erode the boundary more, or less? Why? Be specific.
- In gradually varied flow in a hydraulically wide channel, the flow depth gradient Sy is a function of three parameters. What are these?
- What are the five asymptotic values to which the water surface tend to in gradually varied flow?
- How many types of water surface profiles are they? Which ones are horizontal?
(20%) State six (6) differences between the direct step and standard step methods of steady gradually varied flow computation.
|
Formulas you may need:
So = f F2
So = Sc F2
F2 = v2/ (gy)
q = vy
yc = (q2/g)1/3
|